RFID Parking systems are transforming the way vehicles are managed in urban areas, commercial complexes, and residential communities. These systems use radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology to automate entry, exit, and payment processes, providing a seamless parking experience. By integrating RFID technology into parking management, facility operators can enhance security, reduce congestion, and improve overall efficiency.
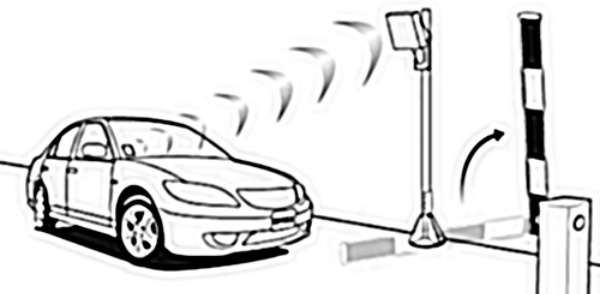
RFID parking systems rely on tags and readers to identify and monitor vehicles. Each vehicle is equipped with an RFID tag, which communicates with a reader installed at entry and exit points. When the vehicle approaches the gate, the reader scans the tag, verifies the credentials, and triggers the access control system. This process eliminates the need for manual ticketing and payment, streamlining vehicle flow and reducing waiting times. RFID parking solutions are suitable for a wide range of facilities, including shopping malls, airports, corporate offices, and residential complexes.
An RFID parking system consists of several key components. The RFID tags, which can be passive or active, store vehicle information and transmit data to the reader. RFID readers are installed at strategic points to detect and authenticate tags. The system also includes access control gates or barriers, software for monitoring and managing parking operations, and payment processing modules for automated billing. Integration with cloud-based platforms and mobile applications allows operators to track occupancy, generate reports, and manage multiple parking sites efficiently.
RFID parking systems offer several advantages over traditional parking management methods. Automation reduces the need for manual intervention, decreasing labor costs and human error. The system enables faster vehicle entry and exit, minimizing congestion and improving user experience. Real-time monitoring of parking spaces helps operators optimize utilization and plan for peak hours. Enhanced security is achieved through unique identification of vehicles, preventing unauthorized access and reducing theft or misuse of parking facilities.
RFID parking systems are widely used in various industries and facilities. Commercial complexes and malls deploy these systems to streamline traffic flow and enhance customer convenience. Airports and transportation hubs implement RFID parking for efficient vehicle management and improved traveler experience. Corporate offices and residential communities use RFID solutions to control access, monitor occupancy, and maintain secure environments. Municipalities and smart city projects also adopt RFID parking systems to manage urban traffic and reduce congestion in public parking zones.
Maintaining an RFID parking system involves regular inspection of hardware components, software updates, and tag replacements as needed. RFID tags are designed to be durable and long-lasting, withstanding environmental factors such as heat, moisture, and physical wear. Readers and gates require periodic cleaning and calibration to ensure accurate detection and smooth operation. A well-maintained RFID parking system provides reliable performance, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of the equipment.
The future of RFID parking is closely tied to smart city initiatives and advancements in IoT technology. Integration with mobile applications, automated payment systems, and real-time data analytics is enhancing the functionality of RFID parking solutions. Future developments may include AI-based traffic management, predictive occupancy tracking, and integration with electric vehicle charging stations. These advancements will continue to improve efficiency, convenience, and sustainability in parking management.
RFID parking systems provide a modern, efficient, and secure solution for managing vehicle access and parking operations. By leveraging RFID technology, facilities can enhance user experience, optimize space utilization, and improve security. With continuous innovation and integration with smart technologies, RFID parking is poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of urban mobility and facility management.